Bi-turbo vs Twin-turbo. Controversy in terminology
Double turbocharger is a unique turbocharging system that allows an internal combustion engine to achieve exceptional agility and high performance. However, this technology is rarely used by motorists who prefer a moderate driving style, which is the majority in our country. That's why many myths and misconceptions have arisen around it.
This technology can be implemented in two main ways: using twin turbo and bi turbo systems. But what is the difference between these terms? Unfortunately, even such reliable sources as Wikipedia and Chat GPT often do not provide unambiguous definitions, which only increases confusion.
Double Turbocharging: Available Types of Turbines and Misconceptions in Definitions
Many mistakenly believe that a twin turbo system is a sequential turbocharging system that uses two different-sized turbines. According to popular opinion, each turbine works in its own range of revolutions, activating in turn and providing sequential operation of the system. On the other hand, they claim that bi turbo is a parallel turbocharging system, where two identical turbines work synchronously and evenly supply air to the engine.
However, such notions are erroneous. The main reason for the confusion between twin turbo and bi turbo is the lack of accurate information in publicly available sources. Incorrect interpretations in articles and advertisements increase misinformation. Also, quite similar terminology in different languages can be interpreted differently, creating even more misunderstandings.
The relevance of the issue is growing as modern cars become more complex and terminology becomes less understandable. Wiatreo company is ready to share knowledge that will help eliminate myths and make an informed decision.
In fact:
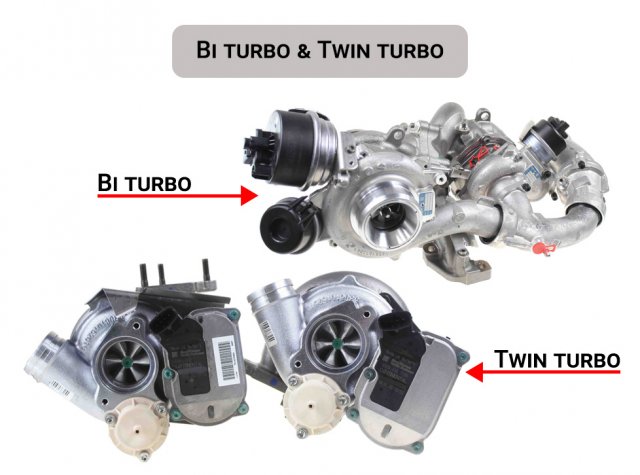
Bi turbo - is a system that uses two turbines connected in series. One of them is smaller and activates at low engine speeds, while the second, larger one, begins to work at high speeds, providing power in the upper range.
Twin turbo - consists of two identical turbines, arranged in parallel and working simultaneously. They evenly distribute the air flow between the engine cylinders, which allows achieving stable power and quick response.
How Does the Twin Turbo System Work?
Initially, this technology was developed for motorsport. Having proven its effectiveness in practice, over time, it was adapted for mass-produced consumer cars. Quite simple mechanics was able to solve the main problem of turbocharging – the appearance of "turbo lag." When installing a large turbine on an engine, a delayed reaction of the car to acceleration (at low speeds) is mainly observed, as a large turbine spins up slowly, which reduces the dynamics of the car. The twin turbo engine variation allows avoiding this disadvantage thanks to the features of its design.
How the Twin Turbo System is Set Up and What Results It Gives
It is based on the parallel operation of two turbines installed opposite each other, each of which is connected to a separate row of cylinders. Therefore, the power of one turbocharger spreads only to half the number of cylinders, resulting in the obtained volume of exhaust gases being sufficient for productive engine operation at both small and large revolutions. For example, in the BMW B58 V6 engine with 335 horsepower, two turbochargers are installed working in parallel:
- the first turbine forces air into one row of three cylinders;
- the second - into another row.
As a result, uniform use of exhaust gases is achieved, which leads to high performance of the internal combustion engine system at both low and high revolutions.
More Examples of Cars with Twin Turbo Systems
Most often, the twin turbo engine is used in internal combustion engines with V-shaped configuration and significant power. In practice, they can be found in such car models:
- Nissan GT-R (R35) with VR38DETT engine: 3.8L V6;
- Toyota Supra Mk4 with 2JZ-GTE engine: 3.0L V6;
- Mercedes-AMG C63, E63, GT, G63 with M177/M178 engines: 4.0L V8;
- Audi RS6, RS7 with 4.0L TFSI V8 engine.
In addition, the Porsche 911 (997 Top) with a 3.6L engine developing 480 hp uses 53049980338 and 53049980337 turbines, which effectively realize the potential of this technology.
BMW's Patented Technology
The twin-turbo system has become an important element of BMW's commercial development. In 2011, the automaker patented this technology, applying it to a four-cylinder 2-liter engine in the BMW X1 xDrive28i model. This solution allowed the creation of a new trademark: BMW TwinPower Turbo.
Twin Turbo Problems and Their Features
Like any complex mechanism, the twin turbo system has its weak points. When operating such technology, the main task is maintaining the correct balance between two turbochargers and ensuring their synchronous operation. If the tuning proves to be insufficiently precise, this can lead to reduced engine performance and malfunctions.
Special attention is required in the following cases:
- The twin turbo system resembles the operation of two separate engines that must function synchronously. If one of the turbines fails, it causes a failure in the overall turbocharging system, and the engine begins to work with violations. Such an imbalance directly affects the dynamics of the car and can lead to more serious breakdowns.
- Difficulties during initial tuning. Replacing the compression impeller on turbines during tuning requires final reconfiguration of the engine. In the case of twin turbo, each part is connected to its own air supply system, where many sensors are used to control the volumes of incoming air. With incorrect calibration, sensors may give errors, and the engine may work unstably.
How Does the Bi Turbo Engine Work?
Bi turbo is a turbocharging system that uses two turbines of different sizes and designs. Unlike twin turbo, where turbines work in parallel, in this case, their work is organized sequentially, which also prevents turbo lag.
The main feature of bi turbo is that turbochargers are activated at different stages of engine operation:
- The smaller turbine starts at low engine speeds. Thanks to its small size and light rotor, it spins up quickly and supplies air to the cylinders, providing an instant response of the engine.
- The larger turbine turns on when the smaller turbocharger reaches its limits. It takes over the supply of more air volume at high speeds, which allows maintaining power and speed at the maximum level.
As a result, the car immediately shows a response to the gas, and the turbo biturbo system provides smooth and powerful acceleration without delays.
Why the Turbo Bi Configuration is Not Suitable for Tuning
Unlike twin turbo, where interference in the system to increase power is permissible, bi turbo is a technology developed exclusively for factory configurations. That is, only automakers can install the biturbo system, designing it in such a way that each turbine has strictly defined parameters – shaft dimensions, compression impellers, manifolds, and throughput.
Attempts at modification are limited to replacing compressor impellers or shafts, but it is impossible to achieve a full upgrade. Also, when changing the parameters of the engine, deep software tuning (chip tuning) is required, which significantly complicates the process.
Cars with Bi-Turbo System: Examples
Bi-turbo is often used in powerful, technologically advanced cars, including passenger and commercial vehicles. This type of engine can be found in:
- Land Rover 3.0 TURBO AJ20D6 (2017-) – a powerful SUV using a two-stage turbocharging system to improve dynamics;
- VW Transporter biturbo T5 2.0L CFCA (2009-) – the turbo bi system allows increasing the efficiency of the diesel engine, improving fuel consumption and dynamics;
- Renault Master dci135 2.3L M9T GEN6 (2019-) – a model known for its reliability, uses the 858864-0004 + 858866-0005 system, which makes it productive under any loads;
- Alfa Romeo Stelvio 2.9 V6 BI-TURBO QUADRIFOGLIO Q4 (2017-) – high power and dynamics, thanks to which the car received sports characteristics.
The bi turbo system is ideal for powerful production cars, as it allows efficiently using the engine's potential at different revolutions. However, due to its complex design and factory settings, it is not intended for active tuning. Manufacturers continue to improve this technology, making it one of the most effective for powerful cars.
Possible Complications with Bi Turbo
Modern automotive engineering strives to maximize the modernization of the bi turbo system, making it more reliable and efficient. However, despite technological developments, it still has weak points. Due to the complex design and interaction of many elements, some problems may occur more frequently than others. They are mainly related to the wear of components, especially those that are subject to frequent mechanical impact:
Wear of Metal Under the Wastegate Valve
Constant metal-to-metal contact leads to gradual abrasion of parts in the valve area. If the wear is insignificant, the engine may fall into a "turbo lag" at low speeds when the small turbine doesn't receive the necessary amount of air. In case of significant wear, the large turbine may receive too much air, causing the internal combustion engine to work unstably, losing power at low speeds or requiring more time to spin up.
Complexity of Actuator Design
The bi turbo system requires the use of several actuators, which complicates the design. The more elements, the higher the probability of breakage. If an actuator fails, the switching valves between turbines may either not open or do so untimely. As a result, the turbine works incorrectly, there may be either insufficient boost (underboost) or excessive boost (overboost), which also negatively affects the engine.
Much less frequently, problems occur with the gas flow switching valve. In the bi turbo system, exhaust gases are dynamically redistributed between the small and large turbines. A special valve is provided for this, which can fail. If the valve gets stuck in the wrong position, one of the turbines simply drops out of the work cycle, resulting in underboost. In another case, a thermal shock caused by excessive pressure is possible.
The Difference Between Bi Turbo and Twin Turbo: Why the Confusion Arises?
Confusion between twin turbo and bi turbo arises due to the similarity of names, although their working principles are different. Twin turbo is a parallel system where two identical turbines work simultaneously, distributing the load between engine cylinders. In bi turbo, in contrast, a sequential scheme is used, where the small turbine is activated at low speeds, and the large one connects at high speeds, providing a uniform power supply. Errors in terminology are often found even in official sources, which creates misunderstanding among car enthusiasts.
